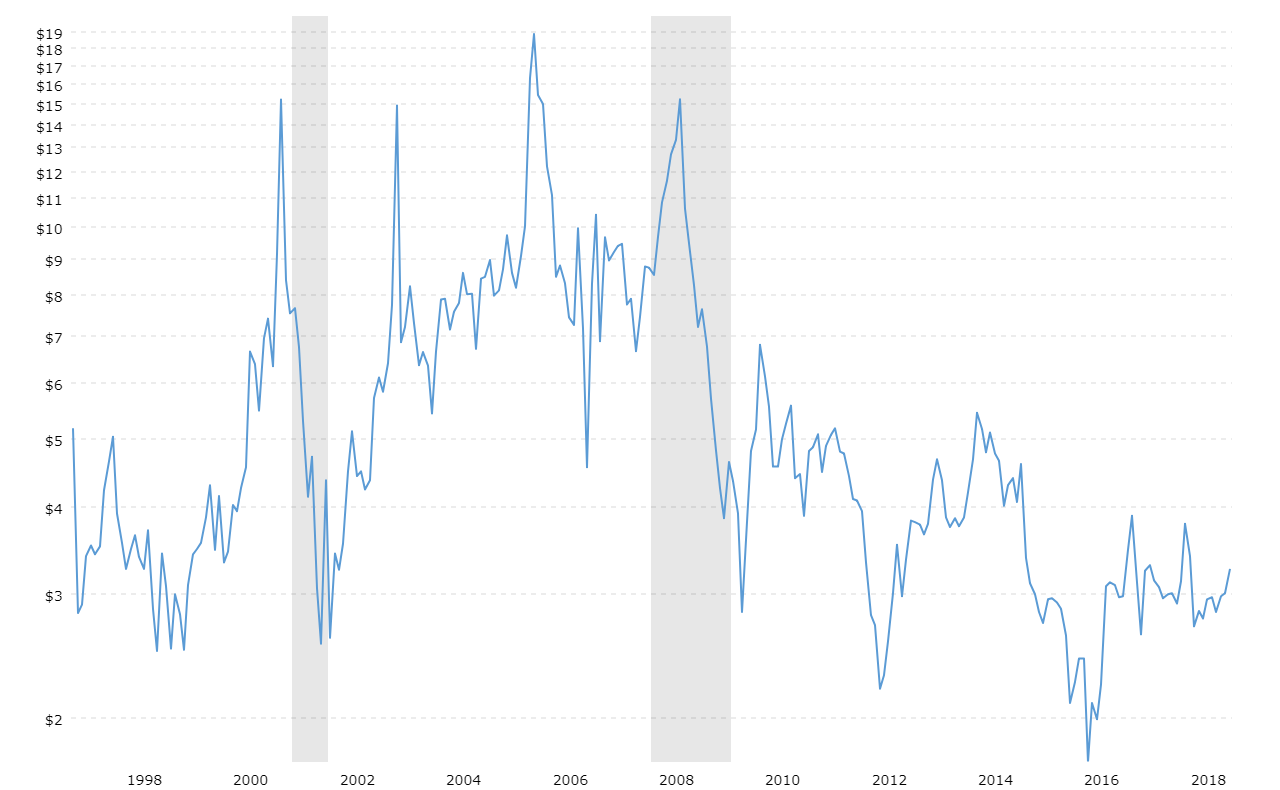
Natural gas is an important energy source for homes and businesses, and its prices can change a lot based on world events. Political tensions, weather changes, and trade rules can affect how much gas is available and how much people want to buy. This makes the market hard to predict. Knowing what affects the supply and demand for natural gas is important for understanding price changes and managing energy costs better.
Geopolitical Tensions and Conflicts
Geopolitical instability often has a profound impact on natural gas markets. Conflicts in major gas-producing regions, such as Russia or the Middle East, can disrupt supply and lead to price spikes. For example, the Russia-Ukraine war in 2022 sent shockwaves through global energy markets, forcing Europe to find alternative sources of natural gas. This resulted in a sharp price rise as nations scrambled to secure supply. Economic sanctions on energy-exporting countries can exacerbate these disruptions, increasing global uncertainty and prices.
Related Blog:
How One Becomes A Natural Gas Broker?
Major Global Events Impacting Natural Gas Prices
Several key events have historically shaped the trajectory of natural gas prices, falling into three primary categories: political, natural, and operational.
Political Events
Natural gas prices are susceptible to political events, as government decisions can directly influence supply and demand. A few examples include:
The Russia-Ukraine War
The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 caused major changes in global energy prices. As countries worldwide imposed sanctions on Russian oil and gas, the prices of these resources went up sharply. By the middle of 2022, the price of oil reached $110 per barrel. At the same time, U.S. crude oil imports dropped by 760,000 barrels per day. Many European countries also stopped buying Russian energy and instead sent it to Asia, which caused even more disruptions in supply chains.
European Energy Storage Crisis
To prepare for the winter months, European Union countries worked hard to increase their gas reserves in 2022. New rules were implemented to ensure gas storage facilities were at least 80% full before winter and 90% complete for the following winters. Even with these efforts, by March 2023, the storage levels were still high at 55%. This was much better than the 26% average 2022, showing that the gas supply can be unpredictable.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The surge in demand for liquefied natural gas (LNG) and pipeline exports led to widespread supply chain disruptions in key industries such as steel production, food processing, and fertilizer manufacturing. Despite increased U.S. natural gas production, supply couldn’t keep up with the growing demand. This imbalance caused natural gas prices to double between February and October 2022.
Weather and Natural Disasters
The weather has a big impact on natural gas prices. When it is very cold in winter or hot in summer, people use more gas for heating or cooling, increasing demand. Natural disasters, like hurricanes, can also damage gas production sites and pipelines, reducing the supply and raising prices. Unpredictable weather or long-term changes in seasons can also cause big changes in gas prices, making it hard to predict how they will move.
Environmental and Climate Change Considerations
Long-term climate change trends may affect the production and consumption of natural gas in unforeseen ways. For example, increasing temperatures may reduce natural gas consumption for heating in colder regions, but it could also lead to higher summer demand for cooling in warmer areas. Furthermore, the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events linked to climate change—such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts—can disrupt production and distribution infrastructure, exacerbating supply shortages and increasing prices.
Related Blog:
Trends in the Natural Gas Market for 2025
Speculation and Investment Market Influence
Speculation in energy markets can also drive volatility in natural gas prices. Commodity traders, hedge funds, and other financial entities can influence the price of natural gas through their buying and selling strategies. Global events often influence these market actors and may exaggerate price swings based on their analysis of political, environmental, and economic developments. This speculative behavior can sometimes cause natural gas prices to experience extreme fluctuations unrelated to immediate supply-demand fundamentals.
Energy Policies and Regulatory Changes
Government policies can also have a lasting effect on natural gas prices. Decisions regarding export restrictions, production incentives, or the transition to renewable energy sources can shift supply and demand dynamics. Carbon taxes and emission rules can help reduce natural gas use over time. These policies can affect both the short-term and long-term, changing how much consumers and industries pay for natural gas.
Rising Heating Demand in Winter
Bad weather, especially in the winter, can significantly affect natural gas prices. When the temperature drops, people use more gas to heat their homes, raising demand and making it more expensive for suppliers to deliver gas. In severe weather, like the Texas winter storm in 2021, gas prices can go up a lot because there isn’t enough gas available.
Operational Costs
Various operational costs influence natural gas prices, ultimately passed on to consumers. Key operational factors include:
Crude Oil Prices
The United States is one of the biggest crude oil producers, strongly impacting oil prices worldwide. When the price of crude oil changes, natural gas prices also often change. Research shows that the connection between oil and natural gas prices is about 25%. This means that if oil prices go up or down, natural gas prices can also change by about 25%.
Refining Costs
Before natural gas can be used, it must be extracted from the ground and cleaned. This process costs money, and the expenses of getting and refining the gas are added to the price, making natural gas more expensive for consumers.
Related Blog:
Key Challenges Facing Natural Gas Brokers Today
Natural Gas Price Trends and Projections
Looking at natural gas price trends over the years, historical data shows significant volatility, especially during events like the European energy crisis 2022. Today, natural gas prices are at an 18-month low, an ideal time for consumers to switch to natural gas as an energy source. The ability to safely store and distribute natural gas makes it a reliable and increasingly affordable option for consumers.
The Future of Natural Gas: Price Projections for Consumers
Looking ahead, several factors will continue to influence the future price of natural gas:
Supply and Demand
As with any market, natural gas prices are dictated by supply and demand. Higher supply leads to lower prices, while a decrease in supply causes prices to rise. Likewise, an increase in demand results in higher prices, and a drop in demand leads to lower prices.
Natural Gas Consumption
In 2023, U.S. natural gas consumption was lower than expected, with an estimated average of 99.1 billion cubic feet per day, down 5% from Q4 2022. This surplus helped drive prices down. At the end of March 2023, U.S. natural gas reserves were expected to be 23% higher than the five-year average, further reducing prices.
International Suppliers
Global natural gas production and imports can also affect domestic prices. When global production increases, prices tend to fall, whereas international shortages can lead to price hikes.
Inclement Weather
Extreme weather events continue to influence price projections. During frigid winters or hot heatwaves, people often pay higher prices because demand for goods increases. Storms and natural disasters that damage supply chains can also raise prices.
Related Blog:
The Future of Natural Gas: What to Expect in the Coming Years
How To Choose The Best Natural Gas Brokerage Firm For Your Needs
Conclusion
Many factors worldwide influence natural gas prices. Political issues, weather changes, energy rules, and new technologies can all affect prices. Events such as natural disasters, changes in energy needs, and global tensions can also make the market unstable. By tracking these factors, consumers and businesses can better understand how energy prices may change and make smarter choices about energy use.