Electricity Capacity Charges
Home » Energy Brokers » Electricity Capacity Charges
Electric grid operators have an important job: they make sure there is always enough electricity for everyone who needs it. This means they have to balance the amount of electricity being made with the amount people use. But this can be hard because energy use changes a lot. It depends on the weather, time of year, the economy, and even world events.
So, how do they ensure there’s always enough power? The answer is electric capacity. This article explains electric capacity, how capacity markets work, and how they help keep our electricity reliable and ready when needed.
What Is Electric Capacity?
Electric capacity is the total amount of electricity plants can produce and provide at any given time. It’s important to have enough electricity ready so everyone who needs it can use it. To help with this, electric grid operators set up capacity markets. These markets encourage power companies to always be ready to produce enough electricity, even when demand is high.
Get Quote
What Are Capacity Markets?
Capacity markets are used in most parts of the U.S. to help make sure there’s always enough electricity for everyone. The only big exception is Texas (ERCOT), though Texas may create one soon.
Here’s how it works:
People and businesses using electricity pay a small fee for their total electricity bill. That money goes to power companies (generators) to help them stay ready to produce electricity, even when it’s not very profitable.
Why is this important?
Sometimes, the price of electricity gets very low, so power companies might not want to make electricity because they wouldn’t make enough money. But we still need electricity 24/7. So, capacity markets pay these companies to be ready to produce power when needed, not just for the power they sell.
This system helps make sure the lights stay on, even when demand is high or prices are low.
Schedule a Consultation with Our Energy Experts
ERCOT Electric Capacity Issues
In February 2021, a big winter storm called Winter Storm Uri hit Texas. It was very cold, and many people needed electricity to stay warm. However, many power plants in Texas stopped working during the storm, so there was not enough electricity for everyone. Some people lost power for many days, and it caused big problems across the state.
This happened because Texas does not have a “capacity market.” In most other states, electric companies get paid just for being ready to produce electricity when needed, even if they don’t always do so. This helps ensure there is always enough power, especially during emergencies.
In Texas, power companies only get paid when they sell electricity. So, they don’t always have a reason to stay prepared for extreme weather.
Texas leaders and ERCOT, the power grid group, are discussing adding a capacity market. This would mean paying power companies to stay ready all the time. The goal is to prevent big blackouts from happening again.
Understanding Capacity Charges
Capacity charges are fees businesses pay for their access to electricity, based on their Maximum Import Capacity (MIC)—the maximum amount of electricity their premises are allowed to use at any given time. These capacity charges reflect the cost of maintaining the infrastructure that ensures electricity availability, even if a business does not always use its full capacity.
How Capacity Charges Are Calculated:
Maximum Import Capacity (MIC)
This is the agreed-upon limit of electricity a business can use. For example, if your business has a 105 kVA capacity, it can use up to 105 kVA of power at any moment.
Capacity Charge
This is the fee per kVA, set annually by the energy regulator (like Ofgem in the UK). For example, if the charge is 2.5p per kVA per day, it represents the cost of the electricity infrastructure needed to provide your maximum capacity.
Monthly Charge Calculation
To find your monthly capacity charge:
Monthly Charge = Maximum Import Capacity (MIC)×Capacity Charge (per kVA/day)×Number of Days in the Month
For instance, with a 105 kVA capacity and a charge of 2.5p per kVA per day, the calculation for a 30-day month would look like this:
Monthly Charge=105×2.5×30=£78.75
Excess Capacity Charges:
If a business exceeds its MIC (e.g., using 130 kVA when the MIC is 105 kVA), it incurs an additional charge for the extra capacity used. This is known as an Excess Capacity Charge.
- Maximum Demand: This is the highest amount of electricity your business uses in a given period. For example, if your maximum demand is 130 kVA, but your MIC is 105 kVA, you’ve exceeded your agreed limit by 25 kVA.
- Excess Capacity Charge Calculation:
Excess Capacity Charge=Excess Capacity×Excess Capacity Charge (per kVA/day)×Number of Days in the Month
If the charge for excess capacity is 2.5p per kVA per day, for a 25 kVA excess over a 30-day month:
Excess Capacity Charge=25×2.5×30=£18.75
This means your business would pay an extra £18.75 for exceeding the limit.
Importance of Managing Capacity:
Businesses should be mindful of their MIC and ensure they don’t consistently exceed it, as doing so could result in significant additional costs. It may be worth renegotiating your MIC or reducing consumption during peak periods to avoid these excess electricity capacity charges.
Managing Power Supply Costs Through Capacity Charge Awareness
Electricity capacity charges, often referred to as power supply capacity charges, play a key role in your overall energy bill, yet they’re frequently misunderstood. These charges are based not on how much electricity you use, but on the highest demand your business places on the grid. For companies looking to reduce capacity charges, it is essential to understand when and how energy is used. By managing peak demand and adopting smarter energy strategies, businesses can significantly lower these often-overlooked costs and improve long-term energy efficiency.
Types of Power Capacity
Power capacity means how much electricity we can produce or save at any time. There are many ways to make electricity, which all add to our total power capacity. Some common sources include:
- Nuclear power plants – use uranium to make heat and create electricity
- Coal – burned to produce energy
- Natural gas – another fuel used to make electricity
- Wind power – uses wind turbines to turn wind into electricity
- Hydroelectric power – uses moving water (like rivers or dams) to make electricity
- Solar power – captures energy from the sun
- Other renewable energy, like geothermal or biomass
But making electricity isn’t the only way to increase capacity. Saving electricity also helps. More power is created when people or businesses use less power because the balance between supply and demand stays the same.
Power companies even have special demand response programs. These programs pay people to use less electricity during busy times, like hot summer days when everyone uses air conditioning.
So, power capacity includes both:
- Making electricity
- Saving electricity by using less
Both help keep the electric grid running smoothly.
Schedule a Consultation with Our Energy Experts
How Is Electrical Capacity Measured and Billed?
Electricity capacity is like a promise to have enough power ready when people need it most. To plan, grid operators (the people who manage the electricity system) hold capacity auctions. These auctions happen up to three years in advance.
Power plants and other energy brokers join the auction and offer to provide a certain amount of electricity during high-demand times, like hot summer days. They must pay a big fine if they can’t keep their promise.

The cost of capacity is included in everyday consumers’ electricity bills. Your electricity provider collects these charges and passes them to the grid operator. The amount you pay is based on how much electricity you use at your highest demand times, measured in kilowatts (kW).
Different areas use different ways to figure this out.
For example:
- In PJM (a large regional grid), your capacity charge is based on your average electricity use during the five hottest days of the summer.
- NYISO (New York’s grid) is based on your highest one-hour use from the previous year.
Your peak electricity use (in kW) is multiplied by the auction rate to figure out your yearly capacity cost. This cost is then included in your monthly electric bills. Because of this, using less power during peak times can help lower your electricity costs and improve your load factor—a measure of how efficiently you use electricity.
Why Is Capacity Important to Consumers?
If you run a business that uses electricity, it’s important to understand how “capacity” affects your power and your bills. In states where energy is deregulated, capacity helps ensure that there’s always enough electricity available when needed. Without enough capacity, you could face power outages or interruptions.
Capacity is also a big part of your energy costs. It can make up around 40% of your electricity supply costs. And since supply costs can be up to 70% of your electric bill, finding ways to lower capacity costs can help save money.
- Get an energy audit to find out where you can save
- Join a demand response program to earn money by using less energy during peak times
- Stagger the start times of motors and equipment
- Switch to energy-efficient LED lighting
- Reprogram your building’s automation systems
- Add solar panels to your building
How Electric Capacity Auctions Work
Electric capacity auctions ensure that there will be enough electricity available in the future, especially on very hot or frigid days when people use much of it. Here’s how it works:
- Looking Ahead: The grid operator (the people who manage the electricity system) looks three years into the future and guesses how much electricity everyone will need.
- Bidding: Power plants, such as nuclear plants, wind farms, and coal plants, offer to provide electricity. Each one says how much power it can provide and at what cost. This is called a “bid.”
- Older plants might offer a lower price because they already paid off most of their building costs.
- Newer power sources usually ask for more money to help cover the building and running costs.
- Choosing Bids: The grid operator arranges all the bids from lowest to highest. Then, they pick just enough to meet future demand, with a little extra just in case. This extra is called a “capacity risk margin.”
- Clearing Price: All the power plants chosen in the auction are paid the same price—the highest price still needed to meet demand. This is called the “clearing price.”
- For example, if the last bid needed to meet demand was from a coal plant at $150 per megawatt, everyone picked—even the cheaper ones—would get $150 per megawatt.
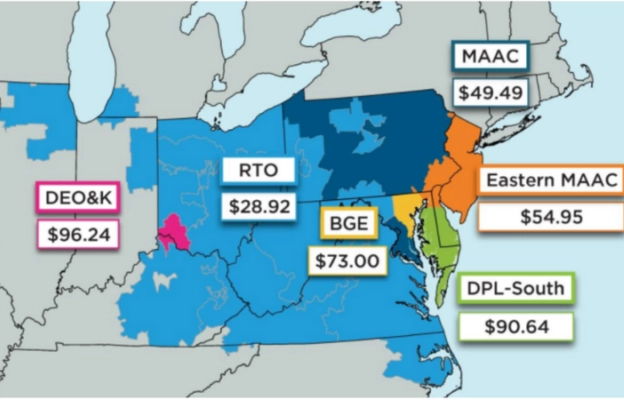
Current PJM Capacity Costs
PJM Interconnection, the organization that manages electricity for many states in the U.S., recently held a capacity auction. This auction ensures that there will be enough electricity available in the future.Most areas saw prices drop by about 15%, which is good news. But in five regions, prices actually went up. This happened because there were limits on how much electricity could be moved (called transmission constraints) and fewer companies offered to supply power.Because of this mix of ups and downs, the total cost of the auction stayed the same at $2.2 billion.
There was also an important rule change during the auction. The government group FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission) approved a change to stop prices from getting too high in one area, the DPL-South Zone.
Even though more than 40,000 megawatts of new power projects have passed the first step to connecting to the grid, problems with supply chains and trouble obtaining land are slowing down the building of new power plants.
A map showing the current prices for each PJM region in dollars per megawatt-hour ($/MWh) is available.
Need Help?
We’re here to help you understand your electricity capacity or manage your energy costs. Our experts at Great Energy 1 are ready to guide you every step of the way. Contact us today to take control of your energy future.
Hear What People Are Saying About Us
Testimonial
