kW vs. kWh: What Is The Difference?
Home » Energy Brokers » kW vs. kWh: What Is The Difference?
The Difference Between Energy Demand and Usage
kW shows electricity demand, and kWh shows electricity use over time. To see the difference, you need to know how energy use is measured. kW shows the power needed at one moment. kWh shows the electricity used over hours or days. Both matter for managing costs and planning how to use power.
Get Quote
What Is a Kilowatt (kW)?
A kW (kilowatt) is a unit of power. Power is the rate of electricity made or used at one moment. A watt measures energy transfer equal to one joule per second. But since “joule” is not used much outside science class, we just say “watt.” Small things like LED bulbs use watts (W). Big things like EV chargers and solar arrays use kilowatts (kW).
One kW equals 1,000 W
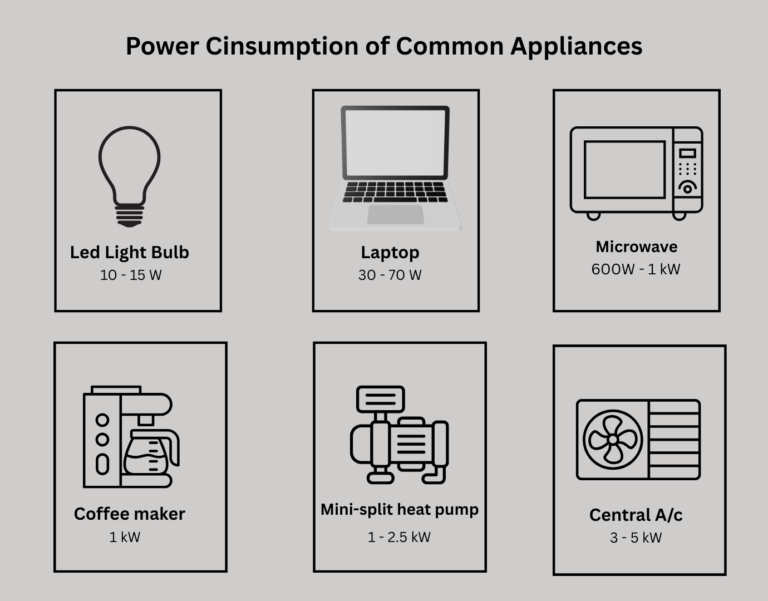
How Do You Calculate kW?
To calculate kilowatts (kW), you need to know the power of a device in watts (W). You can convert watts into kilowatts by dividing by 1,000 because 1 kW = 1,000 W. The formula is simple:
kW = W ÷ 1,000
For example, if a device uses 1,500 watts, the calculation is:
kW = 1,500 ÷ 1,000 = 1.5 kW
This means the device consumes 1.5 kilowatts of power while it is running.
What Is a Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)?
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy. It shows how much energy an appliance uses over time. The formula is: Power × Time = Energy. Power is in kW, and time is in hours. For example, a 1 kW heater running 5 hours uses 5 kWh. If it runs 10 hours, it uses 10 kWh. Your electricity bill is measured in kWh. This is because kWh shows the energy you used in a month. The cost depends on how many kWh you consume.
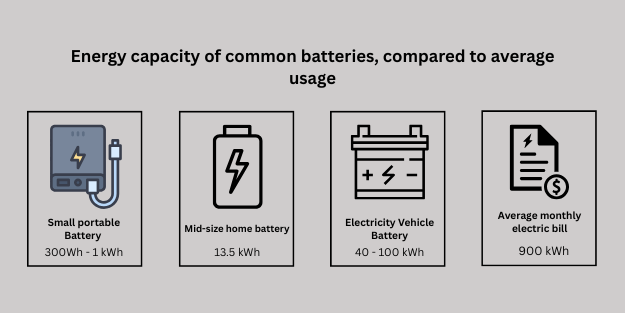
How Do You Calculate kWh?
To calculate kilowatt-hours (kWh), you need two things: the power in kW and the time in hours the device is used. The formula is:
kWh = kW × hours
For example, if a 2 kW electric oven runs for 3 hours, the calculation is:
kWh = 2 × 3 = 6 kWh
This means the oven consumes 6 kilowatt-hours of energy during the 3 hours it is operating.
kW vs kWh: What’s the Difference?
kW shows power at one moment, and kWh shows energy used over time. Think of kW as the “speed” of using electricity. Think of kWh as the “distance” traveled. Knowing the difference helps you read your bill and plan energy use better.
Why Does the Difference Matters?
Knowing the difference between kW and kWh can help you save money. Look at your kWh use patterns. Do you use more power in peak hours? Can you move heavy tasks, like the dishwasher, to off-peak times to cut your bill? Tracking kWh also helps you compare energy plans and pick the best one for you.
Find the best energy plan for your home or business
Factors That Affect Your kWh Use
Many things affect how much electricity you use:
Household size
Bigger families use more power. More people mean more lights, showers, and devices.
Property size
Large homes need more heating or cooling.
Living habits
Working at home, having guests, or long showers increase use.
Season
Bills are higher in summer for cooling and in winter for heating. Holidays can also raise power use.
Typical kW Usage of Home Appliances
| Appliance | Typical kW Usage |
|---|---|
| Blender | 0.5 kW |
| Toaster | 0.85 kW |
| Microwave | 1 kW |
| Vacuum | 1 kW |
| Hairdryer | 1.5 kW |
| Dishwasher | 1.5 kW |
| Dryer | 3 kW |
| Central air conditioner | 3.8 kW |
| Electric water heater | 4.5 kW |
| Slow EV charger | 2 kW |
| Fast EV charger | 7–22 kW |
How Many kW Is In A kWh?
kW and kWh are different units, so you cannot directly convert one to the other without knowing the time. kW measures the power demand at a specific moment, while kWh measures total energy use over hours. The formula to calculate kWh is: kWh = kW × hours. This helps to understand how much energy is used over time and plan better energy management strategies.
What Do kWh & kW Mean For Your Business?
Knowing kWh helps businesses track energy use, save money, and plan upgrades. For example, knowing the kWh of an old air conditioner can show if a new one will save costs. kWh also helps compare power rates, set alerts, and manage bills.
Knowing kW is also important because it shows the peak power a building needs. Cutting peak kW can lower delivery fees, improve ratings, and make a business more efficient. Companies can cut kW by using efficient machines, doing energy checks, joining demand programs, and teaching staff to save power.
How Can I Reduce My kWh Consumption?
Cutting kWh use starts with low-watt items like LED lights and replacing old devices with efficient ones. Turning off unused machines, teaching staff about energy, and shutting HVAC in empty rooms also help. Running heavy machines at different times avoids peak demand. This lowers peak kW and total energy use. These steps help businesses save money and use energy better.
Why Are Kw and Kwh Important?
Knowing the difference between kW and kWh is the first step to managing your energy use. You can check the power draw of your appliances and see how much energy they use over time.
If you want to know how long it takes to charge an electric car, you can multiply the charger’s kW output by the kWh needed for the battery.
These terms are also key for people who want solar panels and batteries. Knowing your power and energy needs helps you choose the right solar and storage system.
Compare your energy use and unlock hidden savings
How Kw and Kwh Are Used in Solar Power?
Knowing the difference between kW and kWh is important when comparing solar quotes. A quote will show system size (in kW), estimated yearly energy (in kWh), and expected bill savings.
System size is the power a solar array can make under standard test conditions (STC). It is measured in kW of DC power. This means the panels give that much power when the sun shines bright.
For example, an array with fifteen 400-watt panels gives a 6 kW system size. When looking at solar quotes, compare systems by kW DC. Your power use decides how many panels you need.
Energy production estimates for solar depend on:
- The system size in kW
- The peak sun hours at your location
- Any shade that lowers output
- The conversion efficiency of your inverter.
Bill savings are then based on the energy produced, your utility rates, and future rate growth.
How Kw and Kwh Are Used for Batteries?
Knowing the difference between kW and kWh is very important when choosing a home battery. A battery is a limited source of energy, unlike the power grid, which has endless supply (unless there is an outage).
Batteries are measured in:
- kWh of storage capacity
- kW of max continuous power output
Calculating Home Battery Size
To size a backup battery, think about these things:
First, know the daily energy use of your key appliances. This shows how much capacity you need. Second, check the power draw of those appliances and make sure the battery output is enough when they all run at once.
This can get complex. Adding volts and amps makes it harder. It’s best to learn the basics of how batteries work so you can talk with a pro who will size and install the system.
Why Is My Kwh Usage So High?
High kWh use can happen for many reasons. Knowing why helps lower costs. One reason is old or inefficient appliances. Old fridges, air conditioners, or water heaters use more energy. Faulty devices can also cause spikes in usage. Heating and cooling are another big factor. Extreme weather makes HVAC systems work harder. Unoptimized thermostats also waste energy. Not using a programmable thermostat or setting the wrong temperature can raise usage. Running many appliances at once adds up to. Using the oven, dishwasher, and air conditioner together increases demand. Energy vampires are another cause. Devices left on standby still use power. Lastly, the weather has a strong impact. Hot or cold days increase heating or cooling needs.
How Can Business Owners Reduce Energy Use?
One way is to upgrade appliances. Use energy-efficient models and think about renewable energy. Another way is to use smart thermostats. Programmable thermostats save power during peak and off-peak times. You can also do an energy audit. A professional check can find areas to fix before making big changes.
Start saving energy and money today
What is the Difference Between Kilowatts and Watts?
The difference between kilowatts (kW) and watts (W) is just quantity. One kilowatt is equal to 1,000 watts. In simple terms, kW is a bigger unit of power than watts.
When to Use kW vs kWh?
Understanding the difference between kW and kWh is the first step. Knowing when to use them is the next step. A kW shows the power an appliance needs to run. This helps when buying things like kettles, coffee makers, heaters, or food processors. The lower the kW, the less power the item needs. kWh, on the other hand, shows how much electricity you used over time. Your power company uses kWh to work out your monthly bill.
How Do You Convert kW to kWh?
The equation to convert kW to kWh is simple: multiply kW by hours used. For example, if you run a 1 kW air conditioner for three hours, it uses 3 kWh of electricity. If it runs for five hours, it uses 5 kWh, and so on.
Hear What People Are Saying About Us
Testimonial
